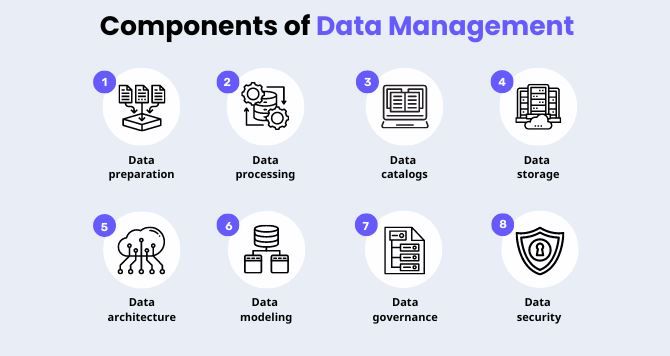
Introduction
In today's world of big data, companies generate and have access to enormous amounts of data than ever before. This data is utilized to make important business decisions through data-driven insights. Investing in data management will be beneficial to companies by bringing in high-quality data that can be used to make critical business decisions.
By implementing data management companies ensure their data is of the highest standard by being accurate, accessible, secure, and compliant with various regulations in the world.
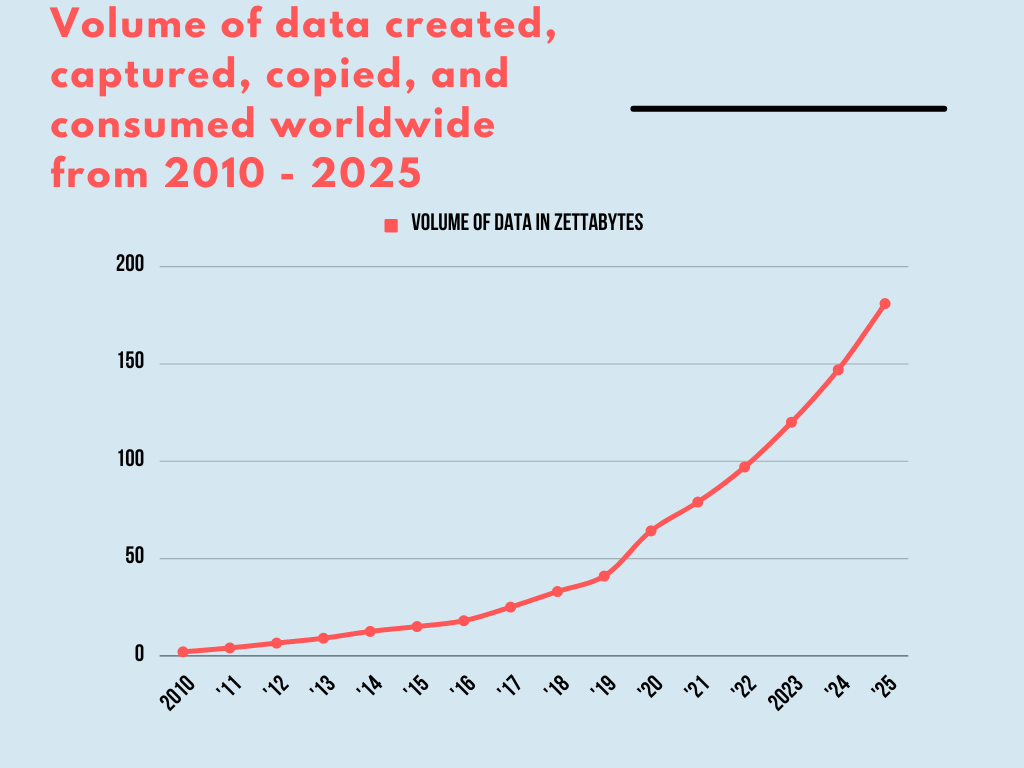
Source: statista
Table of Contents
- Section 1: Overview
- Section 2: The Importance
- Section 3: Challenges
- Section 4: Strategies
- Section 5: Conclusion
Section 1: Overview
What is data management?
Data management is the process in which company data is collected, organized, secured, and stored to be used in analysis and insights to support business decisions. Various tools can be utilized such as databases, data lakes, and data warehouses based on the specific business use case.
Having a well-defined data management strategy allows data science teams to dive deeper into more advanced questions, enabling them to utilize more complex analytical models such as machine learning.
In an article by Exploding Topics, it is estimated that 328.77 million terabytes of data are generated daily.
Section 2: The Importance
The first step in adopting an effective data analysis system at scale is a well-defined data management plan, this results in value added through the form of insightful business decisions.
Scalability
Data management systems allow businesses to scale their data processes automatically while maintaining data consistency and security across the organization. By having repeatable processes companies can avoid duplication of data and prevent unnecessary expenses.
Transparency
Navigating through an organization's data assets can be daunting and challenging if there is no organizational structure. By utilizing data management, companies can increase the usability and visibility of the data which leads to employees finding the right data for their analysis which in turn also leads to more quality and productivity in their jobs.
Consistency
With organizations having multiple departments and each department having their division, there arises the problem of inconsistency in the data information across the organization which leads to confusion and loss of valuable time. However, with data management, there is uniformity and a centralized view of data in one place.
Compliance
When handling consumer data there are certain rules and regulations that companies are required to adhere to which are set by governments and regulatory bodies. By having data management organizations and businesses can stay compliant with CCPA, GDPR, and other data privacy regulation. This is vital to prevent expensive regulatory fines and negative publicity.
Source: SafetyCulture
Section 3: The Challenges
Data Quality
1. Inaccurate Data
To make the right decisions, you need the right data. The challenge of ensuring the data is accurate is immense to the company. Inaccurate data can lead to inaccurate business decisions, deceiving reports, and dissatisfied customers.
2. Incomplete Data
Business decisions are made after analysis is performed on the data. Missing data can lead to inaccurate and skewed analysis. This could further lead to wrong assumptions about KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) and business performance.
3. Inconsistent Data
When working with data across large teams, there must be common standard data definitions and formats to avoid confusion and prevent data discrepancies.
Data Security
1. Data Breaches
A lot of companies handle the personal data of their customers to run their business and operations. When unauthorized personnel or hackers gain access to this data through a vulnerability in the company's system it is defined as a data breach. They do not only lead to compromised data but also tarnish the reputation of the organization. In January 2023 T-Mobile was hacked and data of 37 million accounts was stolen in an API data breach.
2. Unauthorized Access
While data breaches tend to have a more wide-scale issue. A minor issue that could go unnoticed is access by unauthorized individuals within or outside an organization, who can access private information and misuse data. In April 2021, the DC police department reported an "unauthorized access" on its server.
Data Integration
1. Siloed Data
Teams in companies thrive when there is exchange of information between departments. But when this information or data is trapped within a department it can lead to a less comprehensive view on particular processes.
2. Data Fragmentation
As companies grow and the data also grows this leads to the adaptation of new systems, as a result, data becomes fragmented and spread across different platforms. This becomes a challenge as there has to be compatibility between the different platforms used.
Data Volume
1. Big Data
As the volume of data generated and collected increases, company on-premise systems are not capable of handling such large amounts of data. Managing and analyzing such enormous amounts of data require certain tools and technology.
2. Data Overload
If a system is not designed to handle large volumes of data it can lead to slower operations and retrieval speed leading to inefficiencies across the business which can lead to revenue losses. If a well-planned data management system is not in place it would lead to lost revenue. Read this news report by Fivetran and Wakefield Research on the issue of flawed data management.
Data Compliance and Regulations
1. GDPR
General Data Protection Regulation in the European Union has set strict rules and guidelines on the handling and usage of personal data of EU citizens. Companies operating in these regions have to their procedures are compliant with these guidelines or face strict penalties and fines.
2. Other Regional Regulations
While the GDPR is specific to the EU, other places do have their own set of data protection guidelines such as the PDPA in Singapore, the CCPA in California, and so on. Staying afloat and up-to-date with these ever-changing data compliance regulations can be challenging for companies without the right data management.
Data Accessibility
1. Data Retrieval
As the dataset grows, retrieving queried data becomes more time-consuming and slow. As mentioned before with Data Overload, more data is stored in a system not built to handle such a large volume of data. A simple query to retrieve a particular column now takes a longer time. By having the right data management, your company can choose the best data storage for its specific use case. In this article on Towards Data Science, they talk about what you should focus on when choosing a data store.
2. Data Availability
Having downtimes or delays can disrupt business operations and cause inaccurate business decisions. By enabling a continuous and real-time data flow, ensures data is available whenever required by various teams within the organization.
Section 4: Strategies to Overcome Challenges
Implementing Data Quality Tools
1. Data Validation Tools
Deploying software that can validate the accuracy and relevance of incoming data helps prevent unwanted and irrelevant data in the system pipeline.
For example, Informatica Data Quality (IDQ) is a tool that can be used to quickly find and fix data quality issues.
2. Data Profiling
By regularly inspecting the ingested data, companies can learn about its quality, structure, relationships, and inconsistencies. This creates a clear idea of the data cleaning required.
For example, Talend Data Quality is a tool that enables users to profile, cleanse, and mask data while integrating it into business operations.
3. Data Cleaning Solutions
Using automation tools and algorithms that can detect anomalies and correct errors in the dataset, ensuring it remains reliable for decision-making.
For example, Data Ladder's DataMatch Enterprise is a data cleaning solution that provides functions to remove duplicates and maintain clean data.
Implementing Strong Security Measures
1. Encryption
Protect sensitive information from unauthorized access by encrypting it both in transit and at rest.
2. Multi-factor Authentication
MFA (Multi-factor Authentication) implementation adds a layer of security by ensuring that only authorized users can access the data.
3. Regular Security Audits
Checking for vulnerabilities regularly in the data processing and storage systems correcting and patching up any security issues immediately.
Utilizing Data Integration Tools
1. Enterprise Data Integration Platforms
Ensure there is a single source of information by using comprehensive platforms that can gather data from various sources and present it in a unified way.
For example, Microsoft SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) offers a platform that provides a broad range of data migration tasks for various applications.
2. APIs (Application Programming Interfaces)
Use APIs to prevent data fragmentation and silos by facilitating smooth data exchange between various systems and applications.
For example, MuleSoft's Anypoint Platform offers an integration platform that allows developers to connect apps quickly and easily.
3. ETL Processes
Use Extract, Transform, and Load processes to take data from source systems, transform it into a usable format, and then load it into a destination system or database.
For example, Apache Nifi is an integrated data logistics platform from the Apache Software Foundation for automating the movement of data between disparate systems.
Using Data Management Platforms
1. Cloud Storage Solutions
Use cloud-based platforms that can easily scale and provide access while handling enormous volumes of data.
For example, AWS S3 (Simple Storage Service) offered by Amazon Web Services offers a scalable object storage service that can be used for various cases such as data lakes, websites, big data analytics, and data engineering.
2. Data Warehousing
Consolidate data from various sources into centralized repositories to facilitate analysis and reporting.
For example, Snowflake is a cloud-based data warehousing platform that supports different data formats and analytical tools.
3. Automated Backups
Make sure data is regularly and automatically backed up. This ensures business continuity and the avoidance of data loss.
For example, Veeam Backup & Replication provides fast, flexible, and reliable recovery of virtualized applications and data.
Want to learn more about Data Catalog Tools
Check out this article where we get in detail about the use case as well as open-source data catalog tools for modern data management.
Read Now
Implementing Data Governance Policies
1. Data Stewardship
Designate data stewards who will be in charge of ensuring the accuracy, reliability, and security of data throughout the organization.
2. Clear Data Usage Policies
Clear guidelines on how data should be accessed, used, and shared within the organization should be communicated and documented.
3. Regulatory Compliance Monitoring
Keep up with the most recent data protection laws and make sure the business's procedures comply with them. Review and update policies frequently to ensure ongoing compliance.
Section 5: Conclusion
In this article, we looked into the challenges of data management in today's world of data. These challenges are ever-changing along with the data landscape. But by implementing data management into your organization with data quality tools, strengthening security protocols, integrating data sources, optimizing data storage solutions, and emphasizing data governance policies, businesses can effectively navigate this maze.
Companies must not step back and ignore these challenges as the consequences of ignoring them can be far more severe. Effective data management is no longer an option; it is a requirement. Having consistent data monitoring and management cannot be overlooked in an age when data drives decisions, ensures compliance, and fosters innovation. By addressing such issues, organizations can protect themselves from potential risks but also establish a solid foundation for data-driven growth and innovation.
The digital landscape, and thus the way we handle, store, and interpret data, is constantly changing. Businesses must take a proactive approach at this juncture. By implementing robust data management, companies not only overcome challenges but also pave the way for the future of success. Businesses can ensure that they are not only reactive but strategically poised to leverage data's immense potential by investing in robust data management practices now.
Take Your Data Quality to the Next Level!
After delving into data management challenges and their solutions, are you eager to enhance your data quality even further? Learn about a powerful technique that's making waves in the world of data processing. Dive deep into how JSON Schema Validation can play a pivotal role in ensuring impeccable data quality within processing pipelines.
Read "Ensuring Data Quality with JSON Schema Validation in Data Processing Pipelines" now!